Cross-Functional or Layered Process Audit (LPA) in Automotive Manufacturing
🧭 Introduction
Cross-Functional or Layered Process Audits (LPA) are a structured method to ensure that standardized processes are consistently followed and that deviations are identified and corrected quickly. The Cross-functional or Layered Process Audit standard from organization defines the requirements for implementing LPAs across manufacturing operations. This guide integrates OEM expectations, industry standards (AIAG, VDA), and IATF 16949 to help suppliers build a sustainable and effective audit system.
🎯 Purpose
To prevent deterioration of standards and reduce variation by:
- Making deviations visible
- Ensuring immediate corrective action
- Involving management in regular audits
- Driving continuous improvement and accountability
🌍 Scope
This standard applies to:
- All organization manufacturing and assembly sites
- All operations including:
- Production
- Repair and rework stations
- Receiving and shipping docks
- Support functions affecting product quality
👥 Roles & Responsibilities
| Activity | Responsible | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure & resources | General Manager | — |
| Define local LPA procedure | Plant Quality Manager | Cross-functional team |
| Publish audit results | Plant Quality Manager | — |
| Post findings on shop floor | Area Managers, Supervisors | — |
| Maintain checklist content | Quality Engineer | Cross-functional team |
| Maintain audit schedule | Plant Quality Manager | Quality Team |
| Review results | General Manager | Quality Manager |
| Escalate unresolved issues | Area Managers, Supervisors | Quality Manager |
📋 Core Requirements
✅ Documentation & Training
- A documented LPA procedure must exist.
- Employees must be trained, with records maintained.
🧾 Audit Checklist
Each area must have a unique checklist, covering:
- Error Proofing / Detection Device Verification
- First Piece Verification
- Standardized Work Compliance
- Control Plan Adherence
- Gauging and last piece check
- Process settings and parameters
- Customer Interface Characteristics
- Product identification and tagging
- Torque monitoring
- Visual and dimensional inspection
- Documentation and record completion
- Quality Gates
- Packing techniques
- Visual aids
- Corrective action verification
- JES adherence
- Deviations
- Internal and external quality issues
- Top RPN elements from PFMEA
- FIFO compliance
📎 Example Templates: Checklist, Compliance Report, Audit Schedule
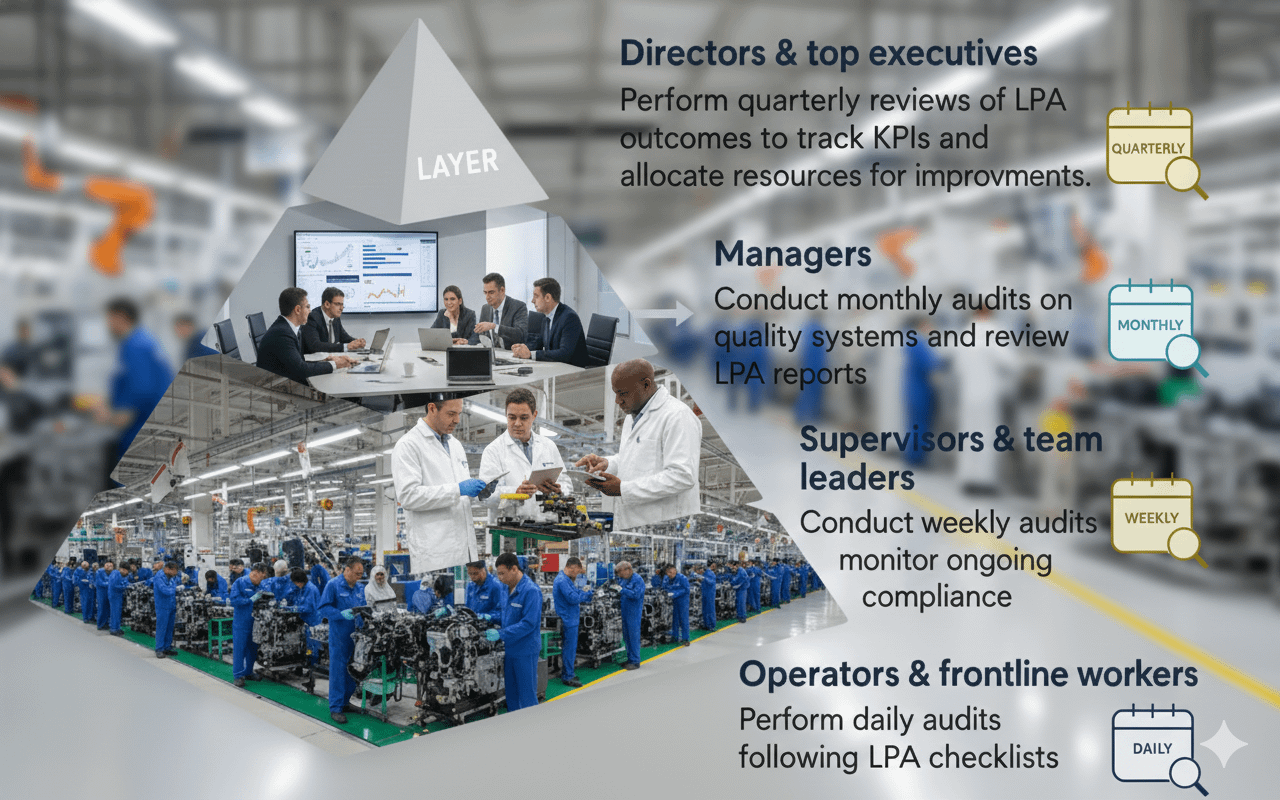
⏱️ Audit Frequency by Role
| Title | Minimum Frequency |
|---|---|
| General Manager / Assistant GM | Monthly |
| Plant Staff (Quality, HR, PC&L, Engineering) | Monthly |
| Area Managers / Engineers | Weekly |
| Supervisors / Team Leaders | Every Shift |
📌 Follow customer-specified frequencies if more frequent.
🚨 Non-Conformance Handling
- Correct within 24 hours if possible.
- If not, escalate to:
- Fast Quality Response Process
- Other tracking systems
- Document all findings and actions.
- Review unresolved items weekly with site leadership.
📊 Data Analysis & Systemic Improvement
- Quality department must:
- Bin findings to identify recurring issues
- Develop action plans for systemic failures
- Audit results and schedules must be:
- Posted in high-traffic areas
- Reviewed regularly by leadership
- Walked randomly by management for verification
📂 Record Keeping
- Maintain records per local plant procedures, including:
- Audit results
- Corrective actions
- Escalation tracking
- Schedule compliance
📚 Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| RPN | Risk Priority Number from PFMEA |
| Error Proofing | Design that prevents defects from occurring |
| Error Detection | Method/device that identifies defects after they occur |
| LPA | Structured audit performed at multiple organizational levels |
✅ Summary
Implementing Layered Process Audits helps suppliers:
- Sustain process discipline
- Identify and correct deviations quickly
- Improve quality and reduce waste
- Meet global OEM and industry standards
📌 Beginner Tip: Think of LPA as your “daily health check” for the shop floor—frequent, visible, and corrective.