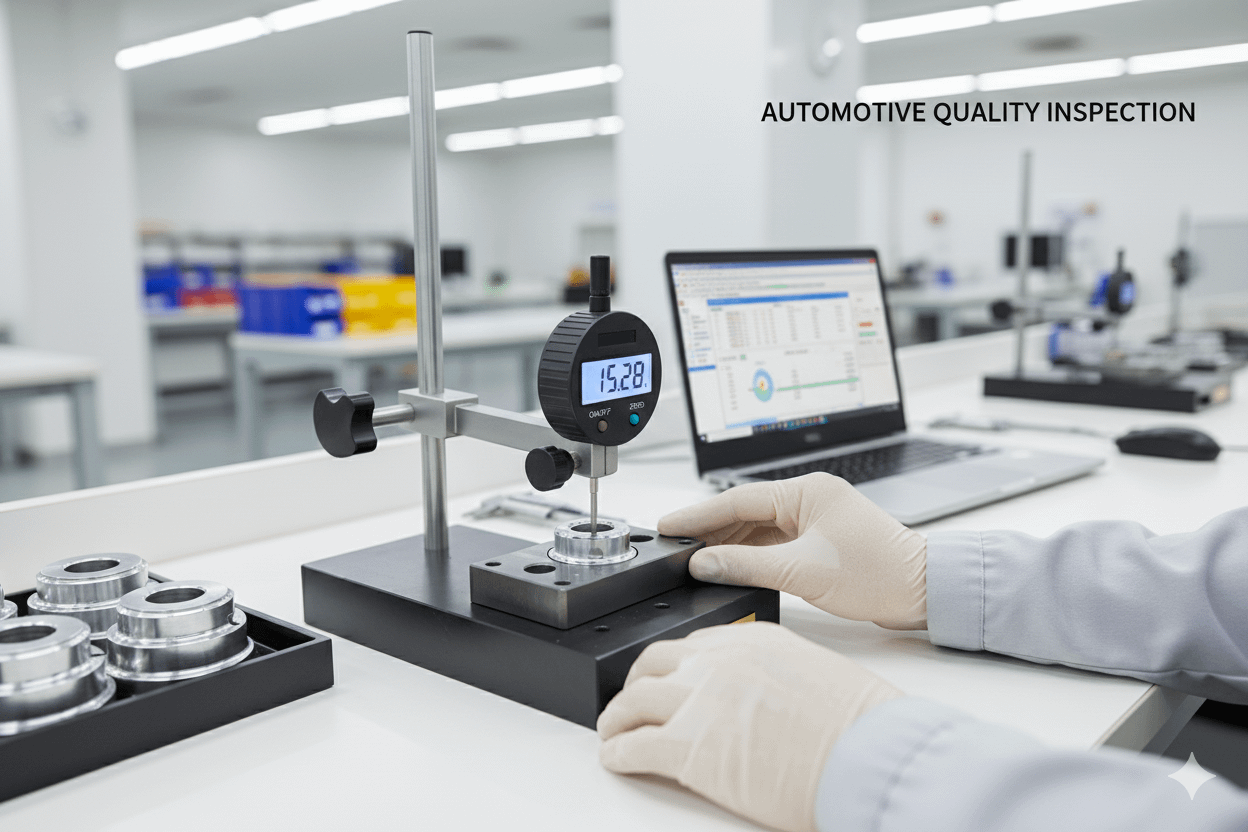

Incoming Inspection Quality Control in Automotive Manufacturing
Incoming inspection is a foundational quality assurance activity in automotive manufacturing. This post outlines the complete framework based on Incoming Inspection, enhanced with best practices from AIAG and VDA standards to ensure global compliance and operational excellence.
🎯 Purpose
To mitigate the risk of non-conforming purchased components entering manufacturing or assembly processes during serial production.
🌍 Scope
- Applies to all suppliers manufacturing and assembly sites.
- Covers incoming materials from external suppliers and internal sites.
- Begins after PPAP approval (interim or full) and continues through end-of-production.
- Every component part number must be inspected at least once per calendar year.
🧑💼 Roles & Responsibilities
| Activity | Responsible | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure & resources | General Manager | — |
| Define local inspection process | Quality Manager | Cross-functional team |
| Release drawings with special characteristics | Product Engineering | Quality, Manufacturing, Program Management |
| Determine part criticality | Supplier Quality Development | Plant Quality, Engineering |
| Measurement system correlation | Supplier Quality Development | Plant Quality Manager |
| PPAP approval | Plant Quality | Supplier Quality Development |
📋 Mandatory Requirements
- Documented procedures and trained personnel.
- Inspection infrastructure: equipment, space, systems, and resources.
- Compliance with non-conforming material handling.
- Annual inspection of all purchased components.
- Measurement system correlation between supplier and organization.
- Process capability data for critical characteristics submitted periodically.
- Duplicate gauges for non-standard features at both supplier and organization sites.
- Supplier rating system based on incidents, PPM, and audits.
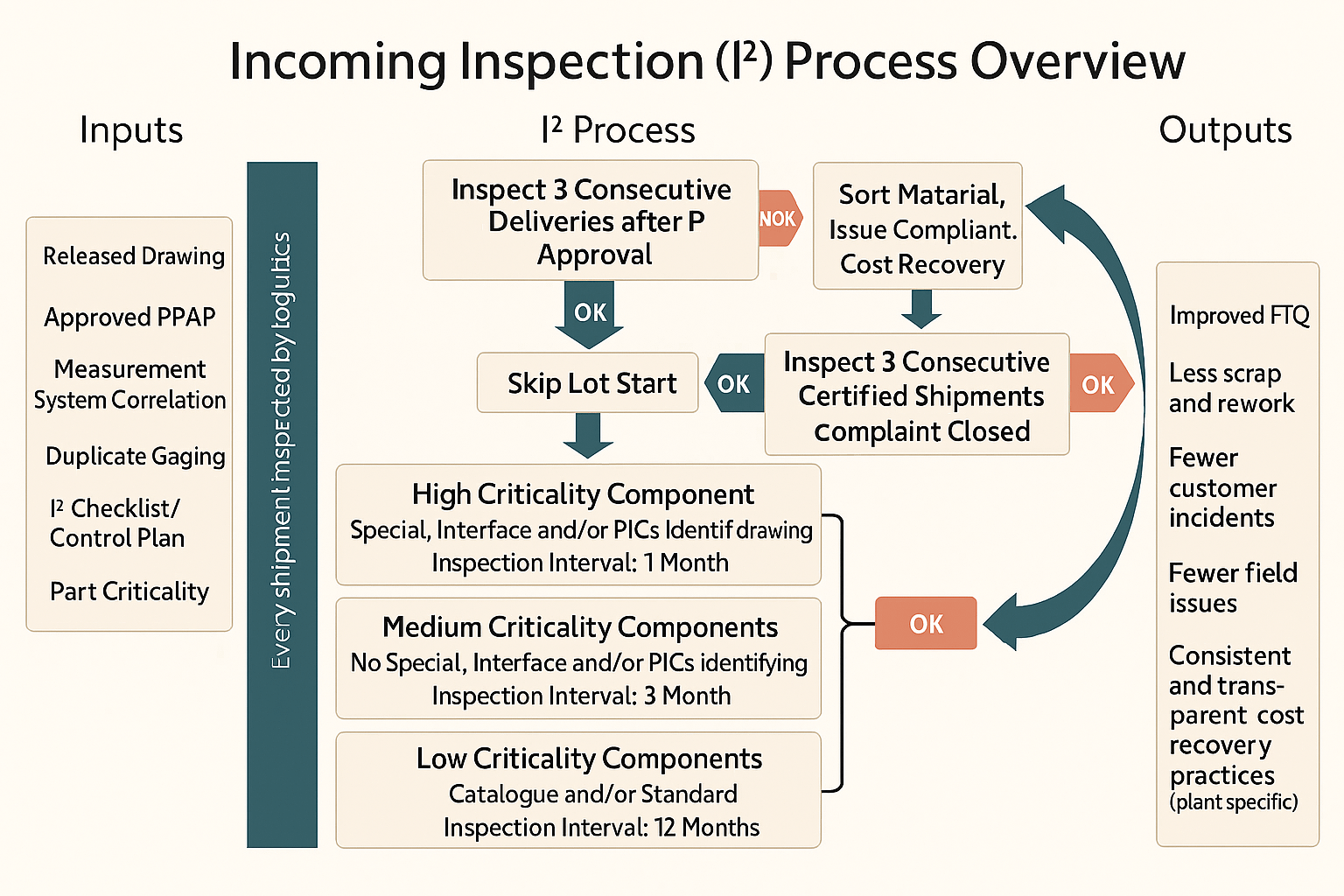
📊 Inspection Frequency by Criticality
| Criticality | Definition | Initial Skip Lot Interval | Post-Complaint Interval | Min. Quantity Inspected |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (H) | Special/Customer Interface Characteristics | 1 Month | 3 OK shipments → 1 Month | 5 Parts |
| Medium (M) | No special characteristics | 3 Months | 3 OK shipments → 3 Months | 3 Parts |
| Low (L) | Standard/catalogue components | 12 Months | 3 OK shipments → 12 Months | 3 Parts |
Skip lot frequency may be adjusted based on statistical capability (Cpk/Ppk) and supplier performance.
🔍 Inspection Activities
Each shipment must be inspected for:
- Labeling and documentation
- Quantity accuracy
- PO description match
- Damage or contamination
Inspections include:
- Visual comparison with PPAP sample
- Dimensional checks of critical features
- Metallurgical testing per drawing
- Confirmation of PPAP status and drawing revision
📑 Control Plan & Records
- A local Incoming Inspection Control Plan must be created post-PPAP approval.
- Must include logistics checks, skip lot frequency, and inspection criteria.
- All inspection records must be maintained per local procedures.
- Deviated shipments must be inspected until deviation expires.
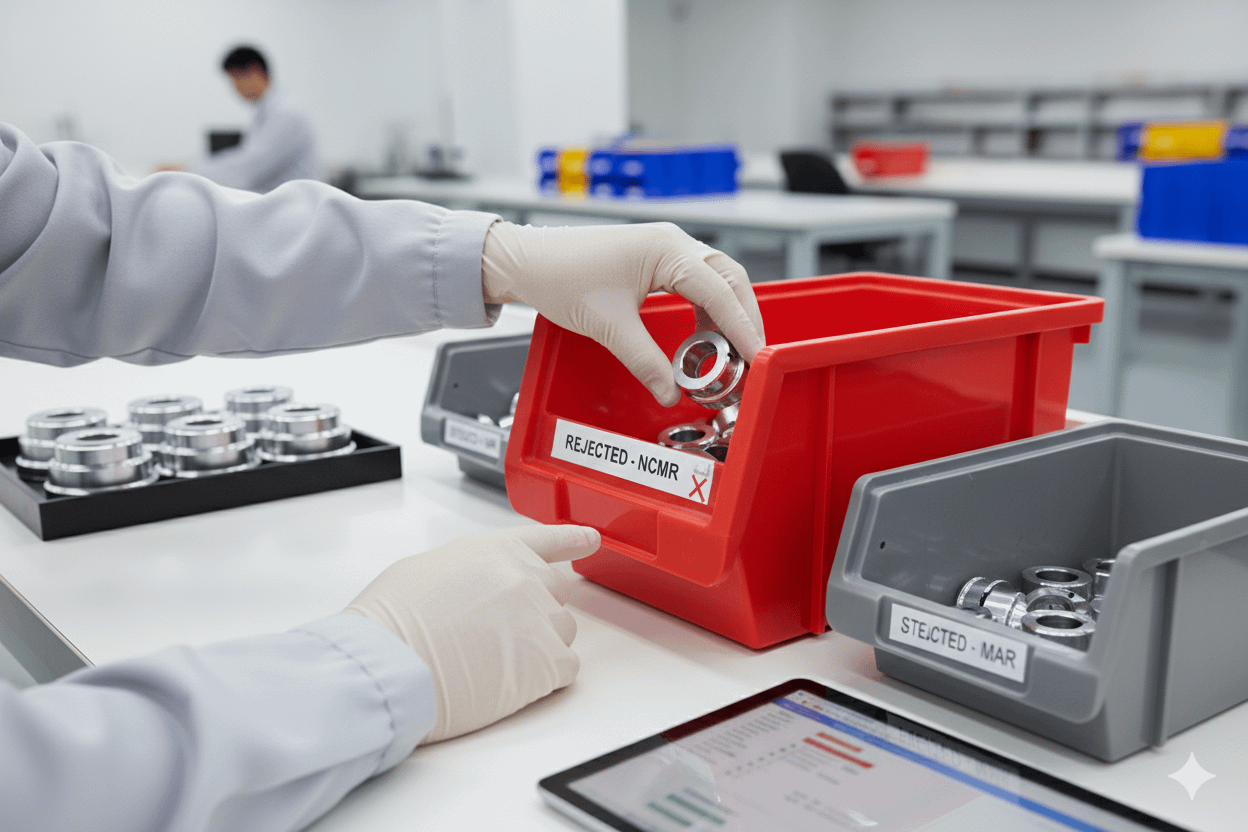
🔄 Complaint Handling & Reinspection
- If discrepancies are found, formal complaints must be issued.
- At least three certified OK shipments are required before resuming skip lot inspection.
- Complaints from the last 3–6 months must be reflected in the control plan.
📘 Integration with AIAG Standards
- APQP & Control Plan: Incoming inspection is a detection control for supplier-related risks.
- PPAP: Ensures supplier readiness and part conformity.
- MSA: Measurement system analysis is essential for correlation and capability.
- CQI Guidelines: Special process assessments (e.g., CQI-9 for heat treat, CQI-11 for plating) support incoming inspection planning.
📗 Integration with VDA Guidelines
- VDA Volume 5: Focuses on measurement and inspection process capability.
- VDA Volume 5.1: Emphasizes inline measuring systems and traceability.
- VDA Practical Guide: Offers real-world applications for inspection planning and execution.
- Risk-based assurance and fine tolerance handling are key VDA principles.
✅ Final Notes
Incoming inspection is not just a gatekeeping activity—it is a strategic quality control function that ensures product integrity, customer satisfaction, and compliance with global standards. By aligning Incoming Insepction Quality Control with AIAG and VDA frameworks, manufacturers can build a resilient and efficient quality system.
📌 Beginner Tip: Treat Incoming Inspection as your “first line of defense”—verify before you trust, and document everything.

Need kèo ma cao 7m? This site is a lifesaver. Always provides the best and most up-to-date odds. Check it out yourself at kèo ma cao 7m.
Alright, Let’s start over again with new chance 123win69. I would like to try some luck here: 123win69
Alright, mates! Checked out da88 and it’s not bad, ya know? Games are decent, and the site’s easy enough to muck around on. Give it a burl! Check it out here: da88