
Causes and Effective Countermeasures
- Causes and Effective Countermeasures
- ✅ 1. Surface Defects
- ✅ 2. Laminations
- ✅ 3. Gas Porosity (Pinholes, Blowholes, Internal Voids)
- ✅ 4. Shrinkage Porosity / Shrinkage Cavities
- ✅ 5. Misrun / Cold Shut / Cold Lap
- ✅ 6. Flash and Gate Residue
- ✅ 7. Die Soldering and Erosion
- ✅ 8. Oxide Film / Inclusion / Dross
- ✅ 9. Hot Tear / Hot Crack
- ✅ 10. Warpage / Distortion and Dimensional Issues
- ✅ 11. Surface Deposits (Black Spots, Oxidation, Contamination)
- ✅ 12. Die Cavity Surface Defects (Blisters, Surface Blowouts)
- ✅ Preventive Quality Management for Automotive HPDC
- ✅ Recommended Quality Criteria for Automotive Components
- ✅ Final Recommendations for Improved Casting Performance
High-pressure die casting (HPDC) is essential in the automotive industry for producing lightweight, high-strength aluminum components with complex geometry and tight tolerances. However, due to the extremely fast filling speed, wide temperature variations, and precise tooling requirements, various casting defects can appear.
In this post, we break down the most common aluminum die-casting defects, explain why they occur, and present practical corrective actions used in automotive-grade production environments.
✅ 1. Surface Defects
What it is:
Irregularities or imperfections on the casting surface (roughness, blemishes, patches).



Common Causes
- Poor die surface condition
- Inconsistent die lubricant
- Contamination or poor cleanliness
Corrective Actions
- Regular die polishing
- Controlled lubricant application
- Shot blasting or surface finishing
✅ 2. Laminations
What it is:
Layers within the casting that do not properly bond, often appearing as layered separations.

Common Causes
- Oxide films trapped between metal flows
- Improper metal handling
- Cold laps or insufficient fusion
Corrective Actions
- Reduce turbulence
- Optimize gating design
- Improve molten metal cleanliness
✅ 3. Gas Porosity (Pinholes, Blowholes, Internal Voids)
What it is:
Porosity caused by hydrogen gas, trapped air, or other gases that cannot escape during solidification.



Common Causes
- High hydrogen content in molten metal
- Turbulent flow during filling
- Oxide films, dross, or inclusions
- Incorrect injection speed profile (too fast/too slow)
- Low intensification pressure or insufficient holding pressure
Corrective Actions
- Degassing (vacuum or rotary), control hydrogen ppm
- Ceramic filtration and surface skimming
- Improve injection profile and reduce turbulence
- Use vacuum-assisted HPDC
- Optimize venting, gate, runner, and overflow design
- Apply X-ray/CT inspection and SPC tracking
✅ 4. Shrinkage Porosity / Shrinkage Cavities
What it is:
Voids created when molten metal is not sufficiently fed during solidification.



Common Causes
- Sudden changes in wall thickness
- Poor feeding path or runner/gate design
- Low holding pressure or insufficient intensification
- Unbalanced temperature distribution
Corrective Actions
- Uniform wall thickness and better thermal control
- Add reservoirs or additional gates
- Increase holding pressure/time
- Use simulation tools to optimize solidification
- Validate with X-ray/CT
✅ 5. Misrun / Cold Shut / Cold Lap
What it is:
Incomplete filling or poor fusion between metal fronts.


Common Causes
- Low injection speed/pressure
- Low molten metal temperature
- Improper gate or runner layout
- Cold spots inside the die
Corrective Actions
- Adjust injection speed and metal temperature
- Modify gate/runner geometry
- Ensure consistent die temperature
- Perform visual and dimensional inspection
✅ 6. Flash and Gate Residue
What it is:
Thin excess metal leaking through parting lines or gate areas.
Common Causes
- Low clamping force
- Excessive injection pressure
- Die misalignment or wear
Corrective Actions
- Verify clamping force
- Maintain die alignment
- Adjust injection pressure
- Standardize trimming operations
✅ 7. Die Soldering and Erosion
What it is:
Molten metal sticks to die surfaces, causing roughness and damage.
Common Causes
- Overheated die surface
- Poor die coating
- Incorrect or inconsistent lubricant usage
- High-reactivity alloy composition (Si/Mg-rich alloys)
Corrective Actions
- Apply nitriding, DLC, or specialized coatings
- Refresh die surface routinely
- Standardize lubricant quantity and spray patterns
- Stabilize die temperature with proper cooling
✅ 8. Oxide Film / Inclusion / Dross
What it is:
Foreign materials such as oxide films or slag trapped inside the casting.
Common Causes
- Turbulent filling
- Poor filtration or insufficient skimming
Corrective Actions
- Molten metal filtration (ceramic filter)
- Proper skimming and degassing
- Optimize runner/overflow design
- Metallographic inspection
✅ 9. Hot Tear / Hot Crack
What it is:
Cracking caused by restricted shrinkage during solidification.
Common Causes
- Complex geometry with limited shrinkage space
- Sharp transitions
- Excessive thermal gradients
Corrective Actions
- Add fillets/radii to reduce stress
- Optimize gate placement for controlled solidification
- Balance die temperature
- Use FEM-based solidification simulations
✅ 10. Warpage / Distortion and Dimensional Issues
What it is:
Unwanted deformation after cooling or heat treatment.
Common Causes
- Uneven cooling
- Improper heat treatment
- Residual stresses
Corrective Actions
- Improve cooling channel layout
- Standardize heat treatment cycles
- Use CMM and SPC to monitor dimensional stability
✅ 11. Surface Deposits (Black Spots, Oxidation, Contamination)
Common Causes
- Oxide inclusions
- Metal contamination
- Excessive lubricant residue
- Operator-related contamination
Corrective Actions
- Maintain cleanliness in molten metal and die
- Implement strict shop-floor hygiene
- Apply washing/shot blasting
- Standardize pre-coating processes
✅ 12. Die Cavity Surface Defects (Blisters, Surface Blowouts)



Common Causes
- Die surface contamination
- Overuse or uneven application of lubricant
- Coating detachment
Corrective Actions
- Recoat and polish die surfaces
- Control lubricant application
- Implement routine die maintenance
✅ Preventive Quality Management for Automotive HPDC
To maintain automotive-grade quality, an effective prevention strategy is essential.
1. Process Capability
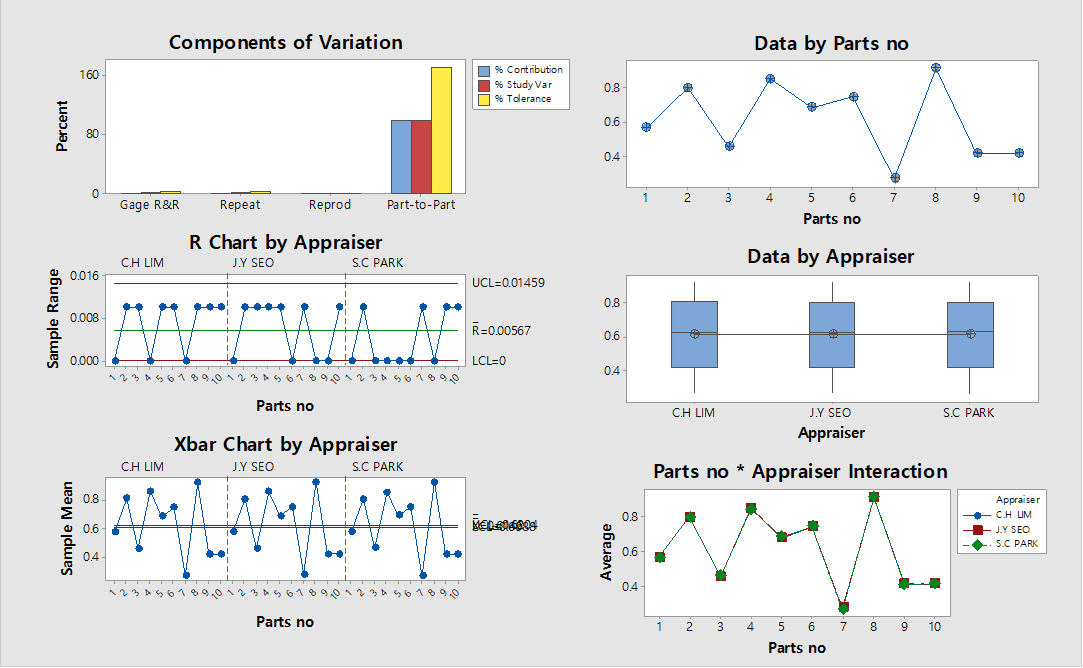
- Monitor Cpk for critical characteristics
- Apply SPC (control charts)
2. Mold Filling & Solidification Simulation
- Use Flow-3D, CAST, MAGMA simulation
- Validate gate/runner/overflow and cooling design
3. Automotive Quality Requirements
- Follow PPAP (Process Flow, PFMEA, Control Plan, MSA, inspection plan)
- Maintain calibration of all measurement equipment
4. Advanced Inspection Techniques
- X-ray and CT scanning
- Metallography
- Hydrogen ppm measurement
5. Structured Problem-Solving
- Containment of nonconforming parts
- Apply 8D and RCA
- Verify permanent corrective actions
6. Training & SOP Standardization
- Train operators on skimming, degassing, lubricant application, and injection control
✅ Recommended Quality Criteria for Automotive Components
- Follow OEM-specific porosity grading standards (X-ray levels)
- Use vacuum-assisted die casting for structural/safety-critical parts
- Follow ISO/ASME dimensional standards
✅ Final Recommendations for Improved Casting Performance
- Prioritize molten metal cleanliness (degassing + filtration)
- Optimize vacuum HPDC and holding pressure
- Implement standardized X-ray/CT acceptance criteria

https://shorturl.fm/MxXeS
https://shorturl.fm/HavDW
https://shorturl.fm/FW7HW
https://shorturl.fm/Vlcut
https://shorturl.fm/PHoBW
https://shorturl.fm/iYuf5
https://shorturl.fm/4aldG
https://shorturl.fm/7FMtX
https://shorturl.fm/OvQcU
https://shorturl.fm/hbuED
https://shorturl.fm/zTFyG
https://shorturl.fm/qtCrQ
https://shorturl.fm/4oXDC
https://shorturl.fm/Xzxq6
https://shorturl.fm/SE1K7
https://shorturl.fm/QFShW
https://shorturl.fm/AhV7g
https://shorturl.fm/pMjJi
https://shorturl.fm/sXAvt
https://shorturl.fm/JVo8D
https://shorturl.fm/yXGnx
https://shorturl.fm/TxC3e
https://shorturl.fm/sHVLM
https://shorturl.fm/wKWTl