Containment Quality Gates in Automotive Manufacturing
🧭 Introduction
In automotive manufacturing, Containment Quality Gates serve as critical control points to detect, contain, and prevent non-conforming products from progressing through the production process. This standard outlines a structured approach to quality control, escalation, and customer protection. This guide integrates OEM expectations, industry standards (AIAG, VDA), and IATF 16949 to help suppliers implement and sustain effective Containment Quality Gate systems.
🎯 Purpose
Containment Quality Gates are designed to:
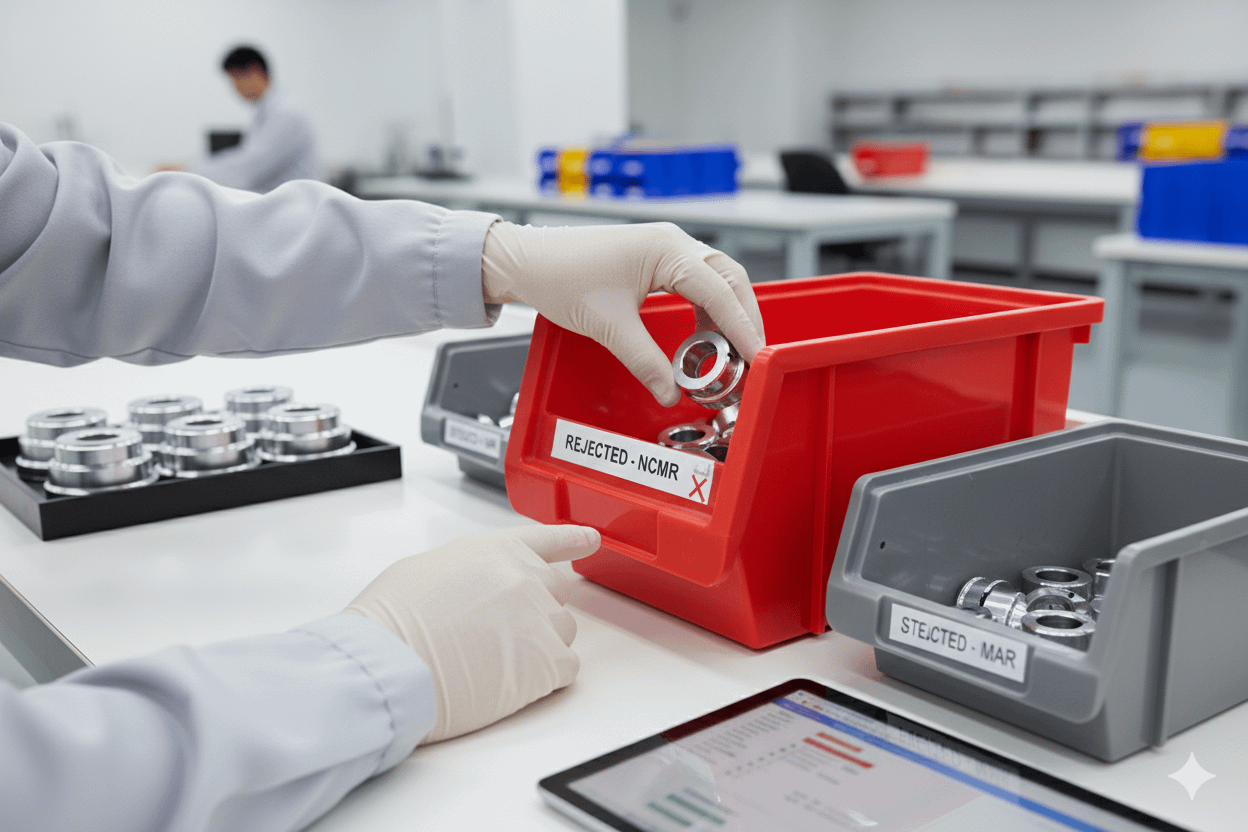
- Detect and contain non-conforming material
- Provide evidence of effective corrective actions
- Support structured problem-solving and escalation
- Protect customer interface characteristics
- Ensure product quality during high-risk conditions
🌍 Scope
This standard applies to all manufacturing and assembly sites and should be implemented:
- At high-risk process points (e.g., Cpk/Ppk < 1.33, high RPN)
- After product or process changes
- In repair/rework areas
- Between departments (e.g., machining to assembly)
- During new product launches (early containment)
- After customer complaints or equipment downtime
Containment Quality Gates may be permanent (e.g., 100% inspection) or temporary (e.g., during safe launch or deviation events).
👥 Roles & Responsibilities
| Activity | Responsible | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure & resources | General Manager | — |
| Define local procedure | Quality Manager | Cross-functional team |
| Post Quality Gate data | Quality Engineer | Plant Quality Manager |
| Analyze non-conformances | Manufacturing & Quality Engineers | Cross-functional team |
| Submit exit request | Quality Engineer | Cross-functional team |
| Approve exit request | Customer or Plant Quality Manager & GM | — |
📋 Core Requirements
✅ Documentation & Training
- A documented Containment Quality Gate procedure must exist.
- Employees must be trained, with records maintained.
🆕 Implementation Triggers
Quality Gates must be implemented:
- For all new programs (minimum 8 weeks post-SOP)
- After customer complaints (internal/external)
- After catastrophic equipment downtime
- When stations are bypassed or under repair
🧱 Physical Setup
- Adequate workspace, lighting, tools, and equipment
- Clear exit criteria posted at the gate
- Located as close to the failure mode as possible
🚨 Escalation & Alarm Limits
- Alarm Limit Escalation must notify:
- Supervisors immediately
- Management within 30 minutes
- Use Gate Alarm Response Sheet to track:
- Escalation contacts
- Timing compliance
- Actions taken
📎 Reference Template: Containment Quality Gate Response Sheet
📊 Containment Quality Gate Documentation
Each Containment Quality Gate must include:
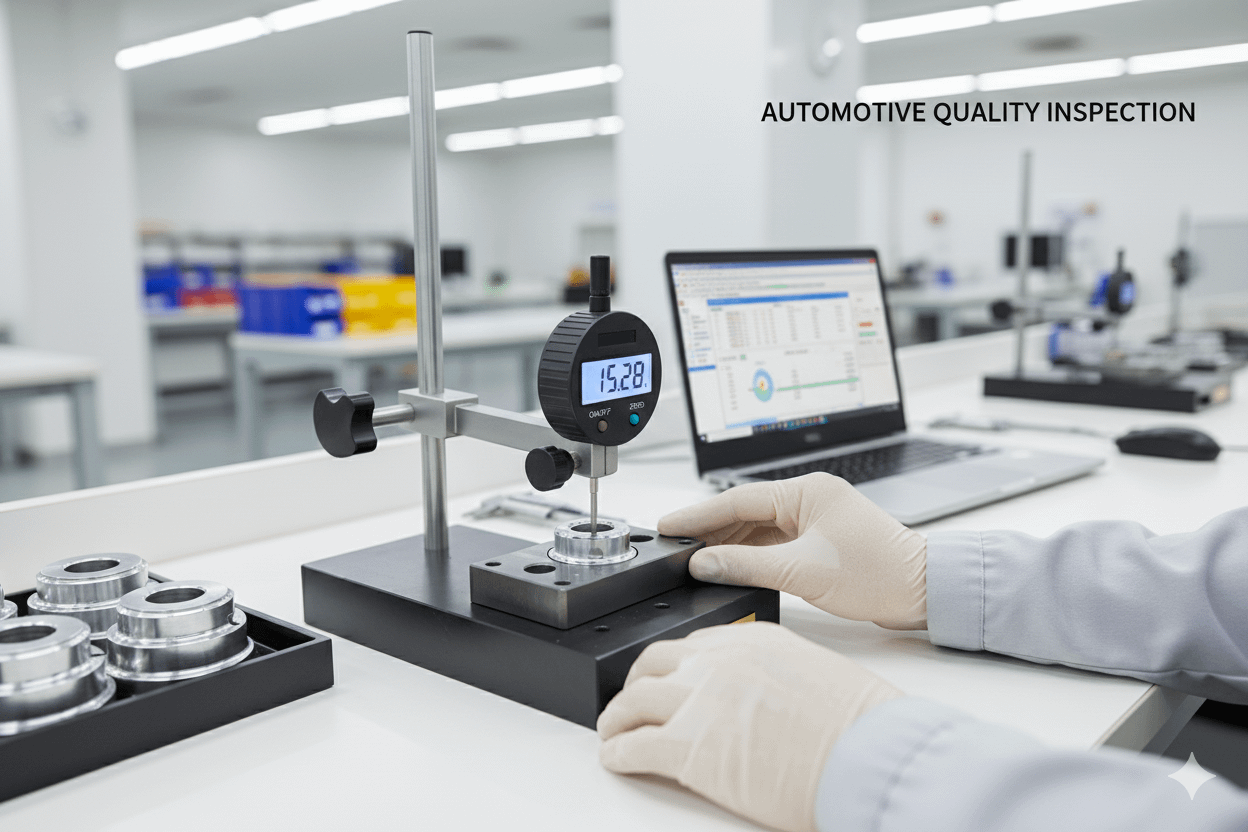
🔍 Inspection Instruction
- Part & drawing number
- Design change level
- Features & specifications
- Inspection method
- Verification mark location
- Cycle time
📎 Reference Template: Inspection standard or Instruction
📈 Tally Sheet
- Failure modes
- Alarm limits
- Inspection date & shift
- Inspector name & signature
📎 Reference Template: Tally Sheet
📉 Incident Chart (“I – Chart”)
- Top 3 failure modes
- Current & prior 3 periods’ data
- Pareto chart
- PPM trend chart
📎 Reference Template: Incident Chart
🔄 Updated weekly, minimum
📋 Gate Alarm Response Sheet
- Escalation process and contacts
- Response timing
- Breakpoint and containment actions
📎 Reference Template: Escalation Process
🧠 Best Practices for Implementation
- Use Standardized Work: Align with Standardized Work for consistency.
- Visual Aids: Include boundary samples or photos for visual defects.
- Gauge Control: Use calibrated variable/attribute gauges.
- Audit Monthly: Plant leadership must audit gates and documentation.
- Track Top 3 Issues: Maintain action plans with timing and ownership.
- Update Weekly: Keep all documentation current and visible.
- Takt Time Compliance: Ensure inspections fit within cycle time.
- Customer Interface Characteristics: Include where applicable to prevent downstream issues.
📂 Required Templates
- Inspection Instruction
- Escalation Process
- Quality Gate Alarm Response Sheet
- Incident Chart
- Tally Sheet
✅ Summary
Implementing Containment Quality Gates helps suppliers:
- Prevent defects from reaching customers
- Improve internal quality control
- Meet global OEM and industry standards
- Support structured problem-solving and escalation
📌 Beginner Tip: Think of Containment Quality Gates as your “last line of defense” before the product reaches the customer. Make them visible, disciplined, and data-driven.