⚙️ Process-FMEA RPN Reduction in Automotive Manufacturing
A Complete Implementation Guide Based on GQS 01 and Global Standards
🧭 Introduction
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a core tool in automotive quality management. The Risk Priority Number (RPN) is used to prioritize risks based on severity, occurrence, and detection. The GQS 01 (V5) standard from Magna Powertrain defines the requirements for reducing RPNs in manufacturing and assembly processes. This guide integrates OEM expectations (GM, Ford), industry standards (AIAG, VDA), and ISO/TS 16949 to help suppliers implement a structured and effective RPN reduction process.
🎯 Purpose
To consistently reduce risk in manufacturing and assembly processes by:
- Identifying high-risk failure modes
- Prioritizing corrective actions
- Ensuring cross-functional collaboration
- Maintaining traceability and auditability
🌍 Scope
This standard applies to:
- All MPT manufacturing and assembly sites
- All MPT-manufactured products
- All process steps including:
- Load/unload
- Storage
- Shipping and receiving
- Rework and outside processing
Implementation must begin within three months after SOP.
👥 Roles & Responsibilities
| Activity | Responsible | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure & resources | General Manager | — |
| Define local RPN reduction procedure | Manufacturing Engineering Manager | Cross-functional team |
| Develop PFMEA before SOP | Advanced Manufacturing Engineering | Cross-functional team |
| Drive PFMEA and RPN reduction | Manufacturing Engineering Manager | General Manager / AGM |
| Maintain RPN Reduction Summary | Manufacturing Engineering Manager | Cross-functional team |
| Approve expense-related actions | General Manager | Assistant GM |
| Implement actions | Manufacturing Engineering Manager | General Manager / AGM |
📋 Core Requirements
✅ Documentation & Training
- A documented RPN reduction procedure must exist.
- Employees must be trained, with records maintained.
🧾 PFMEA Requirements
- A PFMEA must exist for each part number.
- “Family” PFMEAs may be used minimally, with clear differentiation.
- PFMEA must include:
- All print features, specifications, and Customer Interface Characteristics
- All process steps, including non-production activities
- Clear linkage to DFMEA, Process Flow, and Control Plan
- Updates based on:
- Customer/internal failures
- Scrap and rework
- Design and process changes
📎 Reference Template: GQS 01c – Minimum Information Requirements for PFMEA
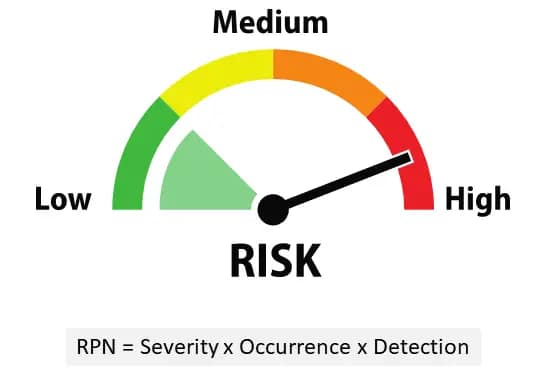
🔢 RPN Calculation & Ranking
- Use AIAG or VDA4 criteria for Severity, Occurrence, Detection
- RPN = Severity × Occurrence × Detection
- High RPNs must be prioritized for reduction
- Reference: GQS 01b – RPN Ranking Table
📊 RPN Reduction Review Process
- Begin no later than 3 months after SOP
- Conduct quarterly reviews, at minimum
- Include cross-functional team (including Product Engineering)
- Maintain evidence (e.g., sign-in sheets, meeting minutes)
📌 RPN Reduction Summary Must Include:
- Top 5 RPN items from PFMEA
- Current and forecasted RPN values
- Process step and failure mode
- Action items, owners, due dates
- Forecasted realization cost
📎 Reference Template: GQS 01a – RPN Reduction Summary
🚨 Handling Non-Feasible Actions
- If RPN reduction is not feasible, document in PFMEA:
- Reason and date in “Recommended Action” section
- Address in Job Element Sheet (JES)
- Maintain 5 active RPN items on the summary at all times
📌 Visibility & Management Review
- Post RPN summary in high-traffic area
- Review by Plant Management (GM/AGM) at least quarterly
- Maintain a recurring review schedule
🔗 Integration with Global Standards
✅ GM & Ford Requirements
- GM: RPN reduction is part of SCCAF, CQI-9, and launch readiness
- Ford: Requires risk mitigation, PFMEA traceability, and Q1 compliance
✅ AIAG & VDA
- AIAG: RPN reduction supports APQP, Control Plan, and FMEA methodology
- VDA 6.3: Requires risk prioritization, action tracking, and audit readiness
✅ ISO/TS 16949
- Requires:
- Documented risk management
- PFMEA linkage to process controls
- Verification of corrective actions
- Continuous improvement
📂 Record Keeping
- Maintain records per local plant procedures, including:
- PFMEA documents
- RPN summaries
- Meeting minutes
- Action item tracking
📚 Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| RPN | Risk Priority Number = Severity × Occurrence × Detection |
| PFMEA | Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis |
| Customer Interface Characteristic | Features critical to OEM assembly or performance |
| Error Proofing | Design that prevents defects |
| Error Detection | Method/device that identifies defects after they occur |
| SOP | Start of Production |
✅ Summary
Implementing a structured RPN reduction process helps suppliers:
- Prioritize and mitigate high-risk failure modes
- Improve product and process reliability
- Meet global OEM and industry standards
- Drive continuous improvement and cross-functional collaboration
📌 Beginner Tip: Think of RPN reduction as your “risk radar”—it helps you spot and fix the biggest threats before they reach your customer.