
Control of Non-Conforming Material in Automotive Manufacturing
🧭 Introduction
In automotive manufacturing, controlling non-conforming material is essential to prevent defective products from entering the supply chain or reaching the customer. The Control of Non-Conforming material standard from organization outlines a structured approach to identifying, containing, evaluating, and disposing of suspect or non-conforming products. This guide integrates OEM expectations, industry standards (AIAG, VDA), and IATF 16949 to help suppliers implement a compliant and effective control system.
🎯 Purpose
To ensure that suspect or non-conforming products are:
- Identified and documented
- Segregated from conforming material
- Evaluated and disposed of properly
- Prevented from unintended use or installation
- Communicated to all relevant internal and external stakeholders
🌍 Scope
This standard applies to:
- All organization manufacturing and assembly sites
- All stages of design, production, and incoming inspection
- Products from suppliers, subcontractors, and customers
- Products already shipped to customers that are later identified as suspect
👥 Roles & Responsibilities
| Activity | Responsible | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Ensure infrastructure and resources | General Manager | — |
| Define local procedure | Plant Quality Manager | — |
| Escalate per GQS 00 if customer impact exists | General Manager or Assistant GM | — |
📋 Core Requirements
✅ Documentation & Training
- A documented procedure must exist.
- Employees must be trained, with records maintained.
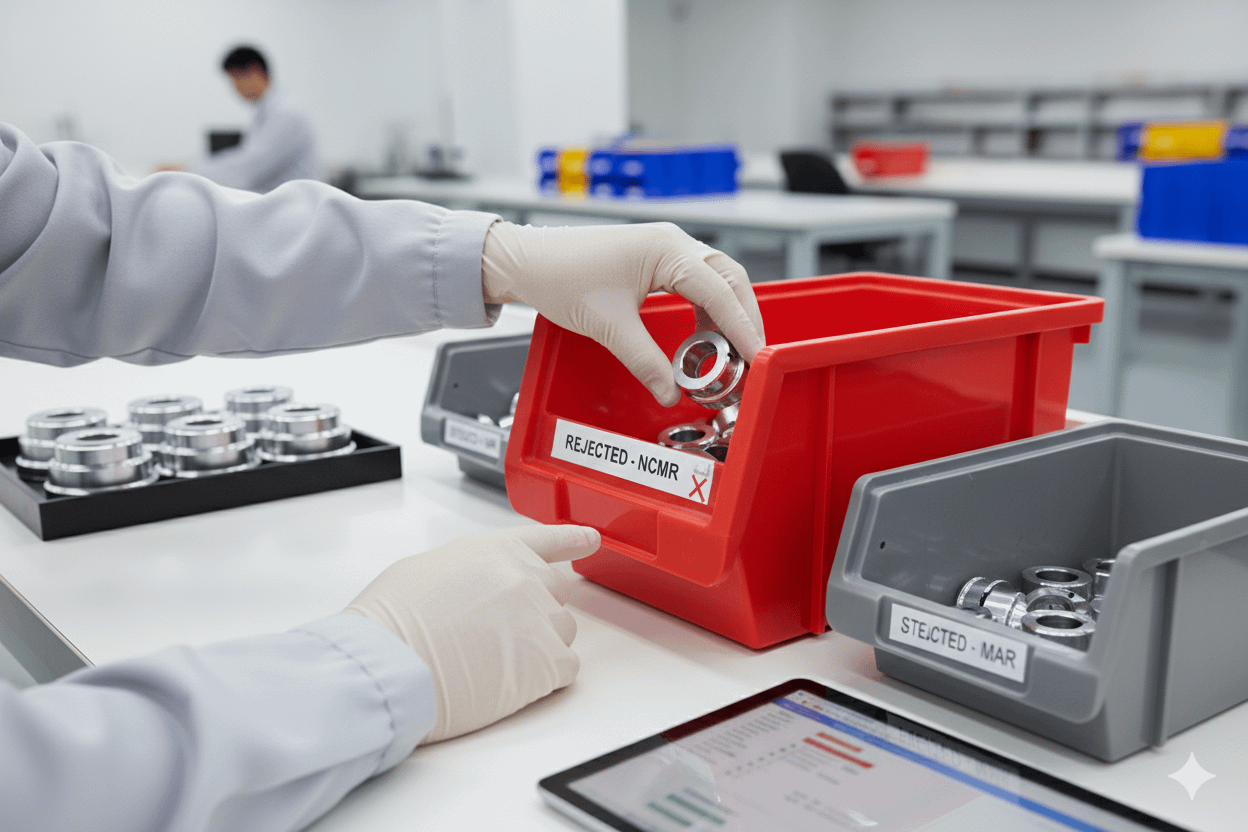
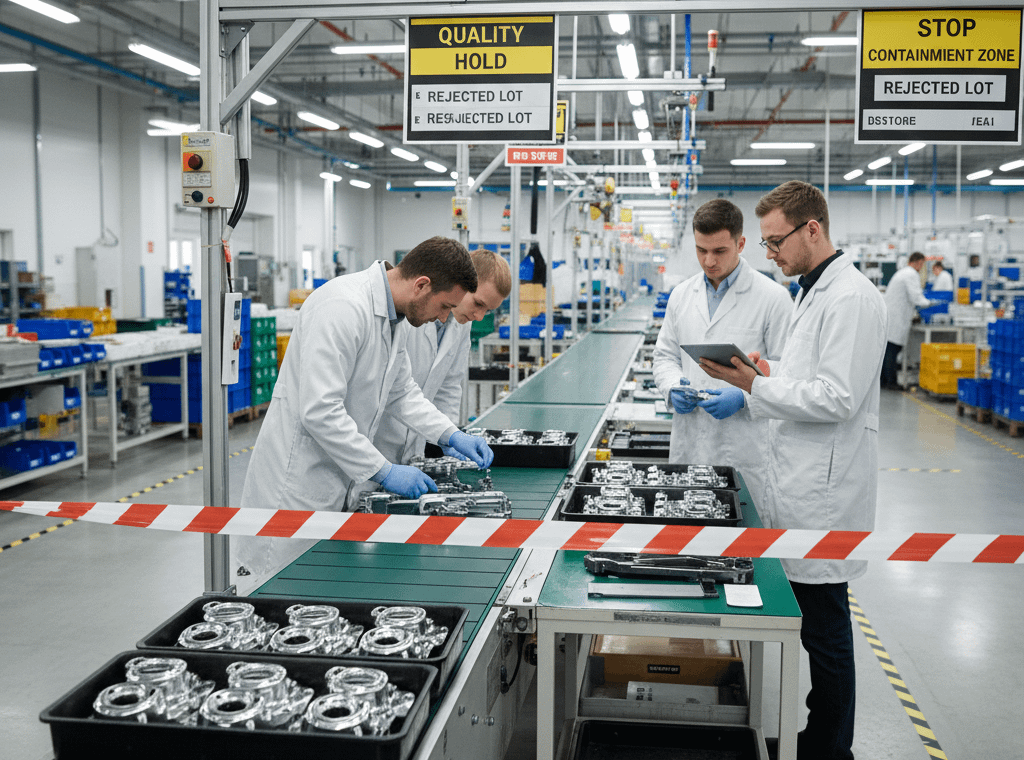
🔍 Identification & Segregation
- Suspect/non-conforming products must be clearly segregated.
- All product containers must be labeled.
- Breakpoints must be defined to separate conforming from non-conforming material.
- Storage and sorting areas must be visibly marked.
- Use red for scrap; red or yellow for blocked inventory.
📎 Reference: Material Identification Standard
🧱 Containment Process
- Use a Containment Worksheet to define all affected areas:
- Internal: machines, fixtures, labs, quality hotels
- External: warehouses, paint, heat treat, sequencers
- Assign a Containment Owner responsible for:
- Execution of containment
- Disposition of suspect material
- Approval of deviations
📎 Reference: Containment Worksheet
📎 Reference: Containment Flowchart
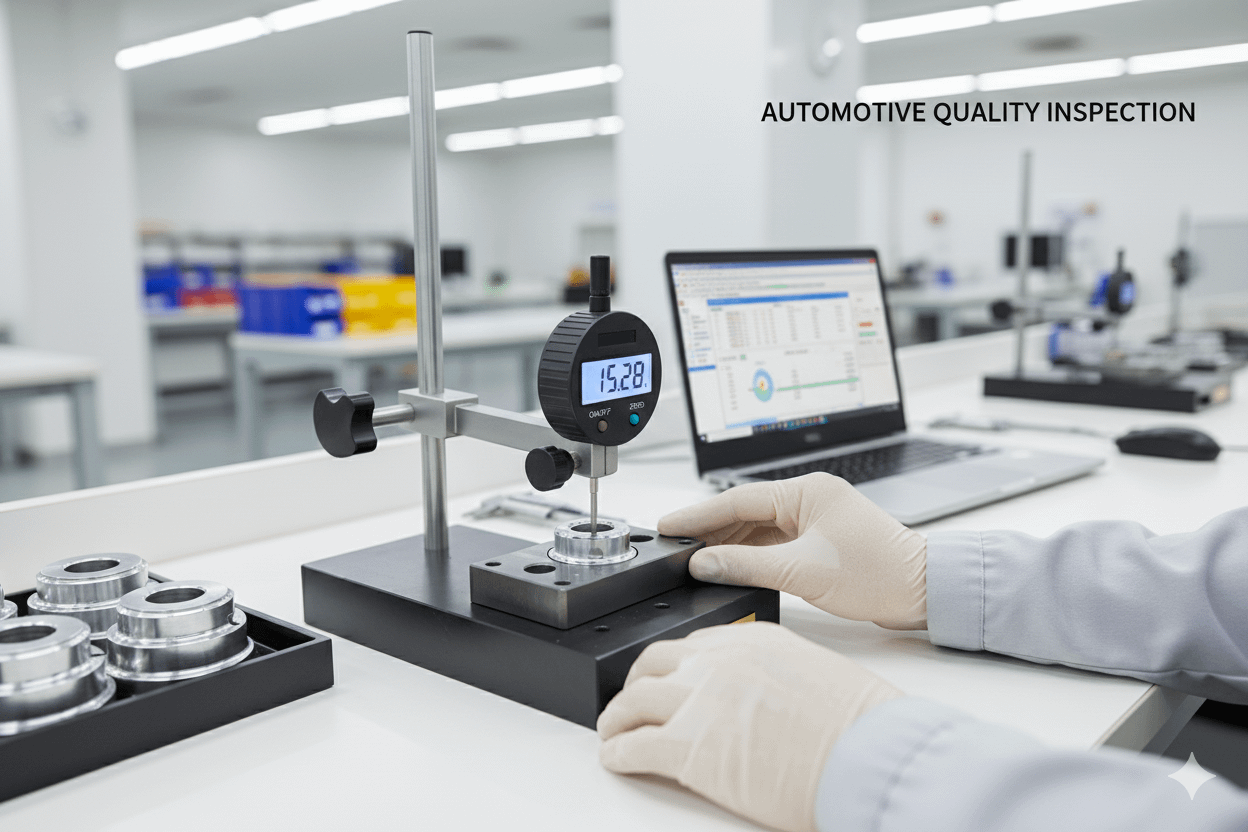
🔁 Rework & Repair Guidelines
- Must be documented using Standardized Work
- Must be approved before starting
- Must be 100% verified using production measurement methods
- If alternate methods are used:
- Conduct an MSA study with acceptable results
- Must have an approved deviation before shipment
📣 Communication & Certification
- Quality Manager must alert all affected customers if containment is incomplete or uncertain.
- Certification of material must confirm it meets print specifications.
- Breakpoints and certification methods must be clearly communicated.
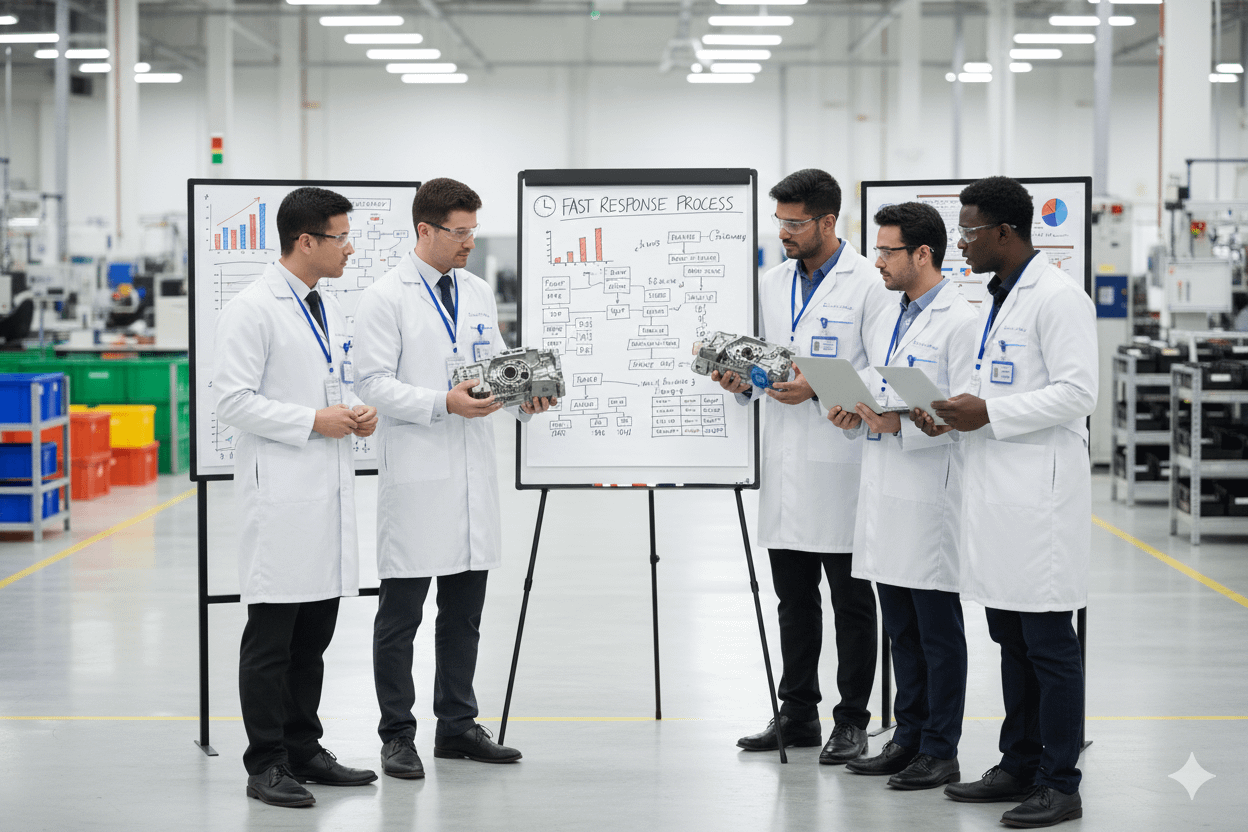
📊 System Integration & Improvement
- Update and link containment actions to:
- D/PFMEA
- Control Plans
- 8D Reports
- Layered or Cross-Functional Process Audits (LPA)
- Containment Quality Gates
- Use these updates to drive systemic improvements and prevent recurrence.
📂 Record Keeping
- Maintain records per local plant procedures, including:
- Completed containment worksheets
- Rework/repair instructions
- Approved deviations
📚 Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Suspect Product | May or may not meet specifications; requires sorting |
| Non-Conforming Product | Does not meet specifications; unusable unless deviation is approved |
| Sorting | Separating suspect from conforming material |
| Containment | Holding suspect material to prevent unintended use |
| Disposition | Final decision on use or rejection of material |
| Breakpoint | Time or point when only conforming material is used |
| Repair | Restoring product using a different method |
| Rework | Restoring product using the original method |
| Certification | Guarantee that material meets specifications |
🔗 References
- Global Escalation Process
- Incoming Inspection Guideline
- Containment Worksheet
- Material Identification Standard
- Containment Flowchart
- Standardized Work
✅ Summary
Implementing a robust Control of Non-Conforming Material system helps suppliers:
- Prevent defective products from reaching customers
- Improve internal quality control and traceability
- Meet global OEM and industry standards
- Support structured containment, rework, and escalation
📌 Beginner Tip: Treat non-conforming material like a quarantine zone—label it, isolate it, and don’t release it until it’s verified and approved.

The PAGCOR portal is pretty solid. Easy to navigate and find what you need. That’s important when you’re trying to stay legit, right? See for yourself pagcor portal
Fun222vip delivers on the promise. Lots of different games and the VIP club seems worth striving for. You should see what fun222vip is all about: fun222vip
Newmacau88… not bad. Standard fare, but the site is easy to use and I had a good time. Check it out if you like the casino atmosphere: newmacau88